Experiment 1
Aim:
To determine the band gap in a semiconductor using its p-n junction diode.
Apparatus required:
p-n junction diode kit, electrical oven, and thermometer.
Formula Used:
The reverse biased current Is (saturated value) is the function of
temperature (T) of the junction diode. For a small range of temperature, the relation is
expressed as,
Log10 Is = constant – 5.036 ΔE (10^3/T)
where, temperature T is in Kelvin, ΔE is the band gap in electron volts (eV).
Theory:
In a semiconductor, there is an energy gap between its conduction and valence band. For the conduction of electricity a certain amount of energy is to be given to the electron so that it goes from the valence band to the conduction band. The energy so needed is the measure of the energy gap (ΔE) between two bands. When PN junction is placed in reverse bias, the current flows through the junction due to minority charge carriers. The concentration of these charge carriers depends on band gap (∆E). The saturation value of reverse current (Is) depends on the temperature of junction diode and it is given by equation,
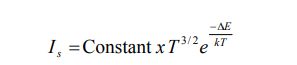
where, k=1.38 x 10-23 J/K is Boltzman’s constant and T is absolute temperature of junction. Taking log of both sides of above equation,

where C is a constant which is equal to the first term of RHS of above equation (for small changes in temperature, log T can be treated as constant). On substituting the value of k and converting the unit of ΔE , we get
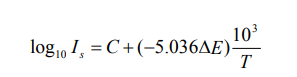
This represents a straight line (y=mx+c) having a negative slope (5.036 ΔE ). Therefore, by knowing the slope of the line, ΔE can be determined through following formula

Procedure:
- Plug the mains lead to the nearest mains socket carrying 230V at 50 Hz A.C.
- Fix a thermometer on p-n junction kit to measure the temperature.
- Keep the temperature switch at OFF position.
- Switch ON the instrument using ON/OFF toggle switch provided on front panel.
- Adjust the voltage (e.g. 5Volt) and note down the reverse current.
- Select the temperature control switch at ON position. Temperature starts increasing and the reading of micrometer also starts increasing.
- As temperature reaches about 78°C, switch off the oven. The temperature will rise further, say about 80°C and will become stable for Ge diode. Note down the maximum reading shown by the micro ammeter (μA).
- Now temperature will begin to fall. Take values of current (in μA) in the interval of 2°C.
- Plot a graph between Log10 Is and (10^3/T) and find the slope.
Observations:
Enter the values of I's for the specified temperatures: